en
names in breadcrumbs


Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklər — filamentar göbələklərdirlər və ona adətən təbiətdə və məişətdə geniş rastlanır . Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklərin coğrafi yayılması çox genişdir (kosmopolitan göbələklərdirlər ) və onların taxıllardan , nəmli binalardan tütündən geniş ayrılması müşahidə edilir . Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklər satratoksinlər kimi tanınan trixotesen mikotoksinlərini əmələ gətirirlər. Bu toksinlər insan yaxud heyvan toxumalarına da toksik təsir göstərə bilirlər .
Ən geniş yayılmış bir növü vardır ki , bu da Stachybotrys chartarum dur .
Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklər təxminən 4 gün ərzində böyüyən pambığabənzər koloniyalar əmələ gətirirlər .Koloniyanın başlanğıc rəngi ağ olur,koloniya yaşlandıqca koloniyanın rəngi qara olur .
Arakəsməli hiflər , konidioforlar , konidilər əmələ gətirirlər .Hiflərdə və konidioforlarda başlanğıcda hialin əmələ gəlir . Yaşlandıqca isə qara piqment əmələ gəlir .

Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklər — filamentar göbələklərdirlər və ona adətən təbiətdə və məişətdə geniş rastlanır . Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklərin coğrafi yayılması çox genişdir (kosmopolitan göbələklərdirlər ) və onların taxıllardan , nəmli binalardan tütündən geniş ayrılması müşahidə edilir . Stachybotrys cinsli göbələklər satratoksinlər kimi tanınan trixotesen mikotoksinlərini əmələ gətirirlər. Bu toksinlər insan yaxud heyvan toxumalarına da toksik təsir göstərə bilirlər .
Stachybotrys és un gènere de fongs (floridures), hyphomycetes per reproducció asexual, fongs filamentosos. Històricament s’ha considerat estretament relacionats amb el gènere Memnoniella,[1][2] Recent,ment, la sinonímia entre els dos gèneres ha estat generalment acceptada.[3] La majoria d’espècie de Stachybotrys habiten en materials rics en cel·lulosa. Aquest gènere està molt estès geogràficament i conté unes 50 espècies.[4] El seu nom prové de les paraules del grec "stakhus" (espiga; σταχυς) o "stachy" (progènie) i "botrus" (grup; βότρυς).
Les espècies més perilloses són S. chartarum (anteriorment coneguda com a S. atra) i S. chlorohalonata, que als Estats Units reben el nom comú de "black mold" (floridura negra) o "toxic black mold" i que estan associades amb una deficient qualitat de l’aire de l’interior dels edificis que sorgeix rere el creixement de fongs en materials dels edificis massa molls.[5] Segons el Center for Disease Control and Prevention, el terme "toxic mold" (floridura tòxica) no és correcte perquè aquest fong en ell mateix no és tòxic ni verinós[6]
Hi va haver una controvèrsia als Estats Units a la dècada de 1990 arran de la mort de dos infants i molts casos més que hi va haver en zones pobres de Cleveland, Ohio degudes a hemorràgia pulmonar que inicialment es va associar a l’exposició a alts nivells de Stachybotrys chartarum. Altres anàlisis posteriors no van trobar aquesta relació.[7]
Stachybotrys és un gènere de fongs (floridures), hyphomycetes per reproducció asexual, fongs filamentosos. Històricament s’ha considerat estretament relacionats amb el gènere Memnoniella, Recent,ment, la sinonímia entre els dos gèneres ha estat generalment acceptada. La majoria d’espècie de Stachybotrys habiten en materials rics en cel·lulosa. Aquest gènere està molt estès geogràficament i conté unes 50 espècies. El seu nom prové de les paraules del grec "stakhus" (espiga; σταχυς) o "stachy" (progènie) i "botrus" (grup; βότρυς).
Les espècies més perilloses són S. chartarum (anteriorment coneguda com a S. atra) i S. chlorohalonata, que als Estats Units reben el nom comú de "black mold" (floridura negra) o "toxic black mold" i que estan associades amb una deficient qualitat de l’aire de l’interior dels edificis que sorgeix rere el creixement de fongs en materials dels edificis massa molls. Segons el Center for Disease Control and Prevention, el terme "toxic mold" (floridura tòxica) no és correcte perquè aquest fong en ell mateix no és tòxic ni verinós
Stachybotrys (/ˌstækiˈbɒtrɪs/) is a genus of molds, hyphomycetes or asexually reproducing, filamentous fungi, now placed in the family Stachybotryaceae. The genus was erected by August Carl Joseph Corda in 1837. Historically, it was considered closely related to the genus Memnoniella,[2][3] because the spores are produced in slimy heads rather than in dry chains. Recently, the synonymy of the two genera is generally accepted.[4] Most Stachybotrys species inhabit materials rich in cellulose. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about 50 species.[5] The name comes from the Greek words σταχυς stakhus (ear of grain, stalk, stick; metaphorically, progeny) and βότρυς botrus (cluster or bunch as in grapes, trusses).
The most infamous species, S. chartarum (previously known as S. atra) and S. chlorohalonata, are known as black mold or toxic black mold in the U.S., and are frequently associated with poor indoor air quality that arises after fungal growth on water-damaged building materials.[6] Stachybotrys chemotypes are toxic, with one producing trichothecene mycotoxins including satratoxins, and another that produces atranones.[7] However, the association of Stachybotrys mold with specific health conditions is not well proven and there exists a debate within the scientific community.[8][9][10]
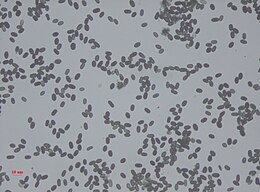
Conidia are in slimy masses, smooth to coarsely rough, dark olivaceous to brownish black, obovoid, later becoming ellipsoid with age, 10–13 × 5–7 mm. Phialides are obovate or ellipsoidal, colorless early then turning to olivaceous with maturity, smooth, 12–14 × 5–7 mm, in clusters of 5 to 9 phialides. Conidiophores are simple, erect, smooth to rough, colorless to olivaceous, slightly enlarged apically, mostly unbranched but occasionally branched. Conidia of Stachybotrys are very characteristic and can be confidently identified in spore count samples. This genus is closely related to Memnoniella. Species of Memnoniella may occasionally develop Stachybotrys-like conidia, and vice versa.[11]
Four distinctive microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) – 1-butanol, 3-methyl-1-butanol, 3-methyl-2-butanol, and thujopsene – were detected on rice cultures, and only one (1-butanol) was detected on gypsum board cultures.[12]
A controversy began in the early 1990s after analysis of two infant deaths and multiple cases in children from the poor areas of Cleveland, Ohio, United States, due to pulmonary hemorrhage were initially linked to exposure to heavy amounts of Stachybotrys chartarum. Subsequent and extensive reanalysis of the cases by the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have failed to find any link between the deaths and the mold exposure.[13][14]
Stachybotrys (/ˌstækiˈbɒtrɪs/) is a genus of molds, hyphomycetes or asexually reproducing, filamentous fungi, now placed in the family Stachybotryaceae. The genus was erected by August Carl Joseph Corda in 1837. Historically, it was considered closely related to the genus Memnoniella, because the spores are produced in slimy heads rather than in dry chains. Recently, the synonymy of the two genera is generally accepted. Most Stachybotrys species inhabit materials rich in cellulose. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about 50 species. The name comes from the Greek words σταχυς stakhus (ear of grain, stalk, stick; metaphorically, progeny) and βότρυς botrus (cluster or bunch as in grapes, trusses).
The most infamous species, S. chartarum (previously known as S. atra) and S. chlorohalonata, are known as black mold or toxic black mold in the U.S., and are frequently associated with poor indoor air quality that arises after fungal growth on water-damaged building materials. Stachybotrys chemotypes are toxic, with one producing trichothecene mycotoxins including satratoxins, and another that produces atranones. However, the association of Stachybotrys mold with specific health conditions is not well proven and there exists a debate within the scientific community.
Stachybotrys es un género de hongos de reproducción asexuada. Relacionado al género Memnoniella,[1][2] la mayoría de las especies de Stachybotrys son mohos que habitan en materiales ricos en celulosa. El género tiene una distribución amplia, y contiene cerca de 50 especies.[3] Las especies de peor reputación, S. chartarum o S. atra, y S. chlorohalonata, son conocidas como moho negro o moho tóxico, y son frecuentemente asociadas con una calidad de aire interna pobre que se acrecienta después del crecimiento de hongos en materiales de edificios y/o construcciones dañados por el agua.[4]
La exposición a la micotoxina presente en Stachybotrys chartarum o Stachybotrys atra puede producir un amplio rango de efectos. Dependiendo de la duración de la exposición y el volumen de las esporas inhaladas o ingeridas, los síntomas pueden manifestarse como fatiga crónica o dolor de cabeza, fiebre, ojos irritados, membranas mucosas de boca, nariz y garganta con estornudos, erupciones cutáneas y tos crónica. En casos severos de exposición o casos exacerbados por reacción alérgica, sus síntomas pueden ser extremos incluyendo náuseas, vómitos y sangrado en pulmones y nariz.[5] La polémica se inició a principios de 1990 tras el análisis de dos muertes infantiles debidas a hemorragias pulmonares en Cleveland, Ohio; vinculadas inicialmente a la exposición a grandes cantidades de Stachybotrys chartarum. Pero nuevos análisis posteriores y extensos de los casos por el Centro para el Control y Prevención de Enfermedades no han podido establecer ninguna relación entre muertes y exposición al moho.[6]
Stachybotrys es un género de hongos de reproducción asexuada. Relacionado al género Memnoniella, la mayoría de las especies de Stachybotrys son mohos que habitan en materiales ricos en celulosa. El género tiene una distribución amplia, y contiene cerca de 50 especies. Las especies de peor reputación, S. chartarum o S. atra, y S. chlorohalonata, son conocidas como moho negro o moho tóxico, y son frecuentemente asociadas con una calidad de aire interna pobre que se acrecienta después del crecimiento de hongos en materiales de edificios y/o construcciones dañados por el agua.
Stachybotrys est un genre de champignons de la famille des Dematiaceae. Il compte, entre autres espèces, une moisissure qui colonise les semences : Stachybotrys chartarum.
C'est un champignon saprophyte qui ne provoque pas de dégât sur les plantes. C'est un destructeur de cellulose que l'on rencontre sur des débris végétaux, sur du papier mais parfois aussi sur des semences[1].
Sur de jeunes plantules, une légère pourriture des germes peut être observée[1].
Toutes les semences peuvent être concernées[2].
Sous forme de spores en surface des téguments[2].
Assez peu fréquent
Colonies mycéliennes peu développées. D'abord blanc-gris puis noir. Les conidiophores sont dressés, bien différenciés, simples, renflés à la base et mesurent de 25 à 100 µm de longueur. Ils se terminent par un bouquet de 6 à 10 phialides qui produisent des spores brun-noirâtre[1].
Selon Catalogue of Life (2 mars 2013)[3] :
Selon Index Fungorum (2 mars 2013)[4] :
Selon World Register of Marine Species (2 mars 2013)[6] :
Stachybotrys est un genre de champignons de la famille des Dematiaceae. Il compte, entre autres espèces, une moisissure qui colonise les semences : Stachybotrys chartarum.
Stachybotrys è un genere che comprende circa 50 muffe appartenenti al phylum degli Ascomycota.[1]
Le specie Stachybotrys chartarum e Stachybotrys chlorohalonata sono conosciute negli Stati Uniti come "muffa nera" o "muffa tossica nera" e sono frequentemente associate a una cattiva qualità dell'aria interna a un edificio, dopo la crescita fungina conseguente a umidità presente nei muri e in generale nei materiali da costruzione.[2]
L'esposizione alle micotossine presenti in S. chartarum (precedentemente nota come S. atra) può avere una vasta gamma di effetti. A seconda della durata dell'esposizione e il volume delle spore inalate o ingerite, i sintomi possono manifestarsi come irritazione in aree differenti, tra cui gli occhi, le membrane mucose della bocca, naso e gola, così come altri sintomi quali starnuti e tosse cronica. In gravi casi di esposizione, o in casi aggravati da reazioni allergiche, i sintomi possono essere estremi e includono nausea, vomito e sanguinamento nei polmoni e dal naso.[3] La discussione è iniziata nei primi anni '90, dopo l'analisi di molteplici casi di bambini delle aree povere di Cleveland, Ohio e di due morti infantili dovute a emorragia polmonare inizialmente legate all'esposizione a notevoli quantità di S. chartarum. Una successiva estesa rianalisi dei casi dai Centri statunitensi per il controllo e la prevenzione delle malattie non sono riusciti a trovare alcun legame tra le morti e l'esposizione alla muffa.[4]
Stachybotrys è un genere che comprende circa 50 muffe appartenenti al phylum degli Ascomycota.
Le specie Stachybotrys chartarum e Stachybotrys chlorohalonata sono conosciute negli Stati Uniti come "muffa nera" o "muffa tossica nera" e sono frequentemente associate a una cattiva qualità dell'aria interna a un edificio, dopo la crescita fungina conseguente a umidità presente nei muri e in generale nei materiali da costruzione.
本文参照
スタキボトリス(Stachybotrys)は、俗にクロカビと呼ばれる糸状菌の1つ。セルロースを好み、浸水や結露などによって高湿度になると住宅に繁茂する。
無色ないし薄い褐色の菌糸から分生子柄が延び、その先端に複数のフィアライドが房状につく。分生子は無節で楕円形からレモン形をしており、成熟とともに暗褐色になる。
本来は土壌などから見付かる腐生菌であるが、家屋内の湿った場所で見出されることが多い。
スタキボトリスはトリコテセン系マイコトキシンのサトラトキシンを産生する。牧草がスタキボトリスに汚染されると、家畜や農夫にサトラトキシンなどによる中毒症を引き起こす。主な症状としては、口腔粘膜や結膜の炎症、壊死性の皮膚炎、鼻血や咳などの呼吸器症状、白血球減少などが挙げられる。サトラトキシンGの経口毒性(LD50)はマウスで1.23 mg/kgとされている。[1]
特にS. chartarum(シノニム:S. atra)は、アメリカ合衆国でtoxic black mold(有毒な黒カビ)と呼ばれている。これは1990年代にクリーブランドで乳幼児の特発性肺出血が流行し、患児の住居でS. chartarumが繁茂していたことがきっかけであるが、CDCの調査の結果ではこの種と肺出血との間に特に関係は認められなかった。[2]この種は確かにマイコトキシンを産生するが、ほかのカビと比べて特に危険というほどではなく、要するに「カビは健康に有害」ということである。[3]
トリコテセン系マイコトキシン以外にも各種の化合物を産生しており、新規薬剤の開発に繋がるリード化合物の起源として期待されている。たとえばStachybotrys microsporaが産生するSMTP-7には血栓溶解作用や抗炎症作用があり、脳梗塞の治療薬としての開発が進められている。 [4]
Stachybotrys elegansにはRhizoctonia solaniを原因とするジャガイモ黒あざ病に対する生物防除効果があることが知られている。[5]ただし本種は狭義のスタキボトリス属には含まれない可能性が高い。[6]
スタキボトリス属には少なくとも70種ほどが知られていたが、[5]分子系統解析によって多系統的であることが指摘され、属の細分化が行われている。[6]
細分化された後の(狭義)スタキボトリス属には少なくとも12種あり、[6]うち主なものを以下に挙げる。
チェコの菌学者Cordaがプラハの壁紙から採取した菌に、1837年Stachybotrys atraと命名したのが最初である。ただしこの菌はエーレンベルクが博士論文(1818年)でStilbospora chartarumと命名したものと同種とされ、したがって現在の学名としてはStachybotrys chartarumとなる。[5]1931年にウクライナで数千頭のウマが中毒を起こし、その原因がスタキボトリスに汚染された牧草であることが判明した。同様の中毒症はその後も東欧諸国を中心に報告されている。1993年にアメリカ合衆国オハイオ州クリーブランドで乳幼児の特発性肺出血が流行し、これ以降住環境でのスタキボトリス汚染について大きな注目を浴びることとなった。[1]