en
names in breadcrumbs


El ratpenat de xarretera llavigròs (Epomophorus labiatus) és una espècie de ratpenat de la família dels pteropòdids. Viu a Burundi, el Camerun, la República Democràtica del Congo, Eritrea, Etiòpia, Kenya, Malawi, Moçambic, Ruanda, el Sudan, el Sudan del Sud, Tanzània, Uganda i Zàmbia. El seu hàbitat natural són els boscos, les sabanes, els arbustars, els manglars i els herbassars àrids i semidesèrtics. No hi ha cap amenaça significativa per a la supervivència d'aquesta espècie.[1]
El ratpenat de xarretera llavigròs (Epomophorus labiatus) és una espècie de ratpenat de la família dels pteropòdids. Viu a Burundi, el Camerun, la República Democràtica del Congo, Eritrea, Etiòpia, Kenya, Malawi, Moçambic, Ruanda, el Sudan, el Sudan del Sud, Tanzània, Uganda i Zàmbia. El seu hàbitat natural són els boscos, les sabanes, els arbustars, els manglars i els herbassars àrids i semidesèrtics. No hi ha cap amenaça significativa per a la supervivència d'aquesta espècie.
Der Äthiopien-Epaulettenflughund oder Temmincks Epaulettenflughund (Epomophorus labiatus) ist ein Fledertier in der Familie der Flughunde.[1] Die Art kommt mit mehreren disjunkten Populationen in Ostafrika vor.[2]
Dieser Flughund ist mit 58 bis 80 mm langen Unterarmen ein mittelgroßer Vertreter seiner Gattung.[3] Bei ausgewachsenen Exemplaren beträgt die Kopf-Rumpf-Länge 108 bis 143 mm, die Hinterfußlänge 18 bis 22 mm, die Länge der Ohren 17 bis 21 mm und das Gewicht 51 bis 99 g. Der Schwanz ist, wenn vorhanden, nur bis zu 5 mm lang.[4] Weibchen sind allgemein etwas kleiner und heller gefärbt als Männchen. Beim hellbraunen Fell der Oberseite besitzen die Haare der Männchen an den Haarwurzeln einen kurzen dunkelbraunen Abschnitt. Das Fell der Unterseite ist bei Männchen überwiegend hellbraun und wird zur Bauchmitte hin weiß. Weibchen haben rosabraunes Fell auf der Brust und etwas dunkleres Fell auf dem Bauch. Namensgebendes Merkmal sind die Epauletten (Schulterstücke einer Uniform) gleichenden weißen Haarbüschel auf den Schultern der meisten Männchen. Zusätzlich kommen bei beiden Geschlechtern weiße Flecken vor und hinter den Ohren vor. Der Kopf ist außerdem durch nackte braune Ohren, große Augen und fleischfarbene Lippen gekennzeichnet. Auf dem Gaumen befinden sich sechs querliegende Wülste. Der Äthiopien-Epaulettenflughund besitzt dunkelbraune Flughäute.[3]
Die nördlichsten Populationen wurden in Eritrea, im zentralen Sudan und im Grenzbereich zwischen Nigeria und Tschad dokumentiert. Im Süden erreicht die Art den Osten der Demokratischen Republik Kongo und das nördliche Tansania. Dieser Flughund lebt im Flachland und in Gebirgen oder Hochflächen bis 2200 Meter Höhe. Er bewohnt feuchte Landschaften in denen Grasflächen, Gebüschflächen und Wälder, wie Regenwälder, Afromontane Wälder oder Miombo-Wälder, ein Mosaik bilden. Nahe der Küste konnte die Art in Mangrovenwäldern registriert werden.[2]
Die Exemplare bilden am Ruheplatz eine kleine Gruppe von etwa 12 Mitgliedern.[2] Sie halten sich dabei kopfüber an den Zweigen von Bäumen oder Sträuchern fest. In dieser Position können sie im Unterholz klettern. Der Äthiopien-Epaulettenflughund fliegt recht langsam im Kronenbereich der Bäume. Wenn die Tiere den Boden erreichen, können sie von diesem den Flug starten. Zur Körper- und Fellpflege werden die poröse Zunge und die Krallen der Hinterfüße benutzt.[3]
Die Nahrung besteht hauptsächlich aus Feigen und anderen Früchten,[3] z. B. aus Myrobalanen (Terminalia), aus Mangos (Mangifera) sowie aus Früchten der Gattungen Irvingia und Salvadora. Komplettierend nimmt dieser Flughund Nektar und Pollen vom Leberwurstbaum (Kigelia africana) und anderen Pflanzen zu sich.[5]
Die Weibchen einer Population in Regionen, in denen zwei Regenzeiten vorkommen, sind zur gleichen Zeit paarungsbereit. Die Geburt des einzelnen Jungtieres und die anschließende erneute Paarung erfolgen zu Beginn der Regenzeiten im März und April sowie im September und Oktober. So ergibt sich eine Trächtigkeitsdauer von fünf bis sechs Monaten. In Gebieten mit einer Regenzeit zwischen November und April erfolgt die Geburt zwischen Oktober und Februar.[5]
Kleinere Populationen können aufgrund von Jagd für den Bushmeat-Markt abnehmen. Der Gesamtbestand wird als stabil eingeschätzt. Die Art wird von der IUCN als „nicht gefährdet“ (least concern) gelistet.[2]
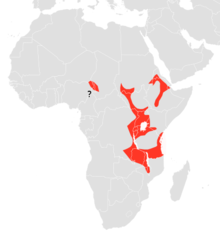 Verbreitungsgebiet des Äthiopien-Epaulettenflughundes
Verbreitungsgebiet des Äthiopien-Epaulettenflughundes Der Äthiopien-Epaulettenflughund oder Temmincks Epaulettenflughund (Epomophorus labiatus) ist ein Fledertier in der Familie der Flughunde. Die Art kommt mit mehreren disjunkten Populationen in Ostafrika vor.
The Ethiopian epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus labiatus) is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Burundi, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. Its natural habitat is savanna.
The Ethiopian epauletted fruit bat is a small, pale brown bat. The only markings on the head are white patches immediately in front of and behind the base of the ear. The snout is long, and the ears are small, rounded and naked. The dorsal fur is dense and fluffy, about 1 cm (0.4 in) long, and extends onto the fore-arm. Males have a light brown pelage, the individual hairs having dark brown bases and pale brown shafts. The ventral fur is paler, the brownish colour fading into the white belly. Adult males have white "epaulettes", but these are normally not visible, being retracted into pouches. Females tend to be smaller and paler than males, having fawn dorsal fur, the individual hairs having beige bases and pale brown tips. The ventral fur is pale fawn on the chest and the belly is darker.[2]
This fruit bat occurs in sub-Saharan Africa, having been recorded from northeastern Nigeria and eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, Chad and South Sudan, eastward to Ethiopia and Eritrea, and southward to Tanzania. It has a patchy distribution, suitable habitat being mosaics of rainforest and savanna.[2] It occurs in both wet and dry forest mosaics, including Afromontane habitats in upland areas around the Great Rift Valley, where it occurs up to about 2,200 m (7,200 ft). It is also found in coastal mangrove forests.[1]
This bat feeds mainly on fruits such as figs, but also consumes leaves. It travels considerable distances in response to the fruiting of different tree species.[3] When moving to new feeding grounds, the flight is fast and direct, but when foraging in the canopy, the flight is slow, with great manoeuvrability, and it can hover briefly. On the ground, locomotion is very awkward, the wings flapping but the hind feet playing no part. It can scramble along branches, and up and down rough surfaces, using its thumbs and hindfeet. The thumb and second finger are opposable and are used to dexterously manipulate food. By day it hangs by its hind feet, usually in some concealed spot, hidden in dense vegetation or under a banana leaf. Several bats may share a common roosting site. It can hang by its thumbs to defecate or urinate. It uses its hind feet to comb its fur, and its long tongue to groom its face, wing membranes and genital region.[2]
This bat has a wide range and is a common species. It is hunted for bushmeat, but otherwise faces no particular threats, and the total population is presumed to be large, so the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".[1]
The Ethiopian epauletted fruit bat (Epomophorus labiatus) is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Burundi, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. Its natural habitat is savanna.
Epomophorus labiatus es una especie de murciélago de la familia Pteropodidae.
Se encuentra en Burundi, Chad, República del Congo, República Democrática del Congo, Eritrea, Etiopía, Kenia, Malaui, Mozambique, Nigeria, Ruanda, Sudán, Tanzania y Uganda.
Su hábitat natural son: sabanas húmedas y secas
Epomophorus labiatus es una especie de murciélago de la familia Pteropodidae.
Epomophorus labiatus Epomophorus generoko animalia da. Chiropteraren barruko Pteropodidae familian sailkatuta dago.
Epomophorus labiatus Epomophorus generoko animalia da. Chiropteraren barruko Pteropodidae familian sailkatuta dago.
Epomophorus labiatus, communément appelé Épomophore d'Éthiopie, est une espèce de chauves-souris de la famille des Pteropodidae.
Epomophorus labiatus, communément appelé Épomophore d'Éthiopie, est une espèce de chauves-souris de la famille des Pteropodidae.
Il pipistrello della frutta dalle spalline etiopico (Epomophorus labiatus Temminck, 1837) è un pipistrello appartenente alla famiglia degli Pteropodidi, diffuso nell'Africa subsahariana.[1][2]
Pipistrello di medie dimensioni con la lunghezza della testa e del corpo tra 90 e 113 mm, la lunghezza dell'avambraccio tra 58 e 80 mm, la lunghezza della coda fino a 5 mm, la lunghezza del piede tra 12 e 18 mm, la lunghezza delle orecchie tre 17 e 21 mm, un'apertura alare fino a 45,5 cm e un peso fino a 64 g.[3]
La pelliccia è corta, soffice e lanuginosa. Il colore generale del corpo è marrone chiaro con la base dei peli più scura e l'addome bianco. Le femmine hanno un colore più fulvo. I maschi hanno due ciuffi di lunghi peli bianchi intorno alle ghiandole situate su ogni spalla e talvolta le spalle e la gola più scure. Il muso è allungato con le labbra e le guance carnose ed estensibili. Gli occhi sono grandi. Le orecchie sono relativamente corte, arrotondate, prive di peli, marroni, con i bordi più scuri e con le caratteristiche macchie bianche alla loro base anteriore e posteriore. Le ali sono marroni e attaccate posteriormente alla base del secondo dito del piede. La coda è molto corta o assente, mentre l'uropatagio è ridotto ad una sottile membrana che si estende lungo la parte interna degli arti inferiori. Sono presenti 6 solchi palatali, gli ultimi due sono post-dentali e divisi in due. Il numero cromosomico è 2n=36.
Si rifugia di giorno singolarmente o in gruppi fino a 40 individui sui rami di alberi o di arbusteti, sotto le fronde dei banani e tra le radici affioranti. il volo è rapido e diretto negli spazi aperti, lento ed altamente manovrato nella vegetazione. Può rimanere sospeso in volo per breve tempo e spiccarlo da terra. I maschi probabilmente effettuano vocalizzazioni notturne di richiamo, tuttavia non rumorose come le altre specie simili e udibili a breve distanza, a causa di una laringe non eccessivamente ingrossata.
Si nutre di frutti di Mango, Kigelia aethiopica, Kigelia pinnata, Irvingia smithii e varie specie native di Ficus.[4]
Danno alla luce un piccolo alla volta due volte l'anno, la prima volta tra marzo ed maggio e la seconda tra settembre ed ottobre. La gestazione dura circa 5-6 mesi.
Questa specie è diffusa nel Sudan del Sud occidentale e meridionale, Uganda, Ruanda, Burundi, Repubblica Democratica del Congo orientale e meridionale, Tanzania nord occidentale, Kenya occidentale, Zambia e Mozambico settentrionali e Malawi. Due popolazioni disgiunte sono presenti lungo il confine tra Ciad, Nigeria e Camerun e un'altra nell'Etiopia centrale e settentrionale e in Eritrea meridionale. È presente anche nell'Arabia Saudita sud-occidentale e nello Yemen occidentale.
Vive nelle Savane alberate, boscaglie e ambienti semi-desertici fino a 2.000 metri di altitudine. Occasionalmente è stato osservato anche nelle mangrovie.[1]
La IUCN Red List,considerato il vasto Areale e la popolazione numerosa, classifica E.labiatus come specie a rischio minimo (LC).[1]
Il pipistrello della frutta dalle spalline etiopico (Epomophorus labiatus Temminck, 1837) è un pipistrello appartenente alla famiglia degli Pteropodidi, diffuso nell'Africa subsahariana.
Epomophorus labiatus is een zoogdier uit de familie van de vleerhonden (Pteropodidae). De wetenschappelijke naam van de soort werd voor het eerst geldig gepubliceerd door Temminck in 1837.
Bronnen, noten en/of referenties
Epomophorus labiatus é uma espécie de morcego da família Pteropodidae.
Pode ser encontrada nos Camarões, República Democrática do Congo, Sudão, Etiópia, Eritreia, Uganda, Quênia, Burundi, Ruanda, Tanzânia, Maláui, Moçambique e Zâmbia.
Epomophorus labiatus é uma espécie de morcego da família Pteropodidae.
Pode ser encontrada nos Camarões, República Democrática do Congo, Sudão, Etiópia, Eritreia, Uganda, Quênia, Burundi, Ruanda, Tanzânia, Maláui, Moçambique e Zâmbia.
Epomophorus labiatus[2][3][4] är en däggdjursart som först beskrevs av Coenraad Jacob Temminck 1837. Epomophorus labiatus ingår i släktet Epomophorus och familjen flyghundar.[5][6] IUCN kategoriserar arten globalt som livskraftig.[1] Inga underarter finns listade.[5]
Pälsen är allmänt ljusbrun. Framför och bakom varje öra finns en vit fläck. På hannarnas axlar förekommer tofsar som påminner om epåletter. Dessutom är hannar ofta lite mörkare och större än honor. De korta avrundade öronen är nästan helt nakna.[7] Arten når en kroppslängd (huvud och bål) av 108 till 143 mm och svansen är bara en upp till 5 mm lång stubbe eller den saknas helt. Epomophorus labiatus har 65 till 80 mm långa underarmar, 18 till 22 mm långa bakfötter och 17 till 21 mm långa öron.[8]
Denna flyghund förekommer i östra och centrala Afrika. Utbredningsområdet sträcker sig från Sudan och Etiopien till östra Kongo-Kinshasa, östra Zambia och norra Moçambique. Möjligen finns en isolerad population i södra Tchad. Arten vistas i låglandet och i bergstrakter upp till 2000 meter över havet. Habitatet utgörs av skogar, savanner med trädansamlingar, torra gräsmarker med buskar och mangrove. Vid viloplatsen bildar individerna en liten flock.[1]
Individerna vilar i träd eller buskar och håller sig fast på kvistar och grenar. När de avsöndrar urin eller avföring håller de sig fast med tummarna så att bakkroppen hänger ner. Annars sover de med huvudet neråt. Arten äter främst fikon och andra frukter.[7]
Epomophorus labiatus är en däggdjursart som först beskrevs av Coenraad Jacob Temminck 1837. Epomophorus labiatus ingår i släktet Epomophorus och familjen flyghundar. IUCN kategoriserar arten globalt som livskraftig. Inga underarter finns listade.
Pälsen är allmänt ljusbrun. Framför och bakom varje öra finns en vit fläck. På hannarnas axlar förekommer tofsar som påminner om epåletter. Dessutom är hannar ofta lite mörkare och större än honor. De korta avrundade öronen är nästan helt nakna. Arten når en kroppslängd (huvud och bål) av 108 till 143 mm och svansen är bara en upp till 5 mm lång stubbe eller den saknas helt. Epomophorus labiatus har 65 till 80 mm långa underarmar, 18 till 22 mm långa bakfötter och 17 till 21 mm långa öron.
Denna flyghund förekommer i östra och centrala Afrika. Utbredningsområdet sträcker sig från Sudan och Etiopien till östra Kongo-Kinshasa, östra Zambia och norra Moçambique. Möjligen finns en isolerad population i södra Tchad. Arten vistas i låglandet och i bergstrakter upp till 2000 meter över havet. Habitatet utgörs av skogar, savanner med trädansamlingar, torra gräsmarker med buskar och mangrove. Vid viloplatsen bildar individerna en liten flock.
Individerna vilar i träd eller buskar och håller sig fast på kvistar och grenar. När de avsöndrar urin eller avföring håller de sig fast med tummarna så att bakkroppen hänger ner. Annars sover de med huvudet neråt. Arten äter främst fikon och andra frukter.
Epomophorus labiatus — вид рукокрилих, родини Криланових.
Країни поширення: Бурунді, Камерун, Демократична Республіка Конго, Еритрея, Ефіопія, Кенія, Малаві, Мозамбік, Руанда, Судан, Танзанія, Уганда, Замбія. Він був записаний від низовини до висот понад 2000 м над рівнем моря. Пов'язаний з рідколіссям (в тому числі міомбо ліс), саванами, чагарниковими заростями, посушливими і напівпустельними пасовищами. Відпочиває в невеликих групах близько десятка тварин.
Як видається, немає серйозних загроз для цього виду в цілому. Деякі групи населення можуть виявитися під загрозою надмірного полювання для їжі. Цей вид був зареєстрований з багатьох природоохоронних територій.
Epomophorus labiatus — вид рукокрилих, родини Криланових.
Epomophorus labiatus là một loài động vật có vú trong họ Dơi quạ, bộ Dơi. Loài này được Temminck mô tả năm 1837.[2]
Phương tiện liên quan tới Epomophorus labiatus tại Wikimedia Commons
Epomophorus labiatus là một loài động vật có vú trong họ Dơi quạ, bộ Dơi. Loài này được Temminck mô tả năm 1837.
에티오피아견장과일박쥐(Epomophorus labiatus)는 큰박쥐과에 속하는 박쥐의 일종이다.[1] 부룬디와 차드, 콩고공화국, 콩고민주공화국, 에리트레아, 케냐, 말라위, 모잠비크, 나이지리아, 르완다, 수단, 탄자니아 그리고 우간다에서 발견된다. 자연 서식지는 건조 사바나 지역과 습윤 사바나 지역이다. 서식지 감소로 멸종 위협을 받고 있다.